Postpartum Hemorrhage
Define post partum haemorrhage. List the causes of postpartum haemorrhage. Explain the treatment and nursing care of postpartum haemorrhage.
Definition
More than 500 ml of blood loss following normal vaginal delivery or 1000 ml following Caesarian section
Hemorrhage leading to a fall in hematocrit by 10%
Incidence
1-4%
PPH Risk Factors
Abnormalities of uterine contraction (Tone) : polyhydramnios, multiple gestation, macrosomia, rapid labor, prolonged labor, high parity, intraamniotic infection, fibroid uterus, placenta previa, uterine anomalies
Types of Postpartum hemorrhage
Primary
Bleeding within 24 hrs of delivery
Primay is of 2 types
Third stage hemorrhage : bleeding that occurs before the expulsion of the placenta
It occurs in placenta accreta, placenta increta placenta percreta and retained placenta
True postpartum hemorrhage : bleeding after the expulsion of placenta
Secondary
Also called delayed or late postpartum hemorrhage
Bleeding after 24 hours to 6 weeks of delivery
Etiology
Causes of primary postpartum hemorrhage :
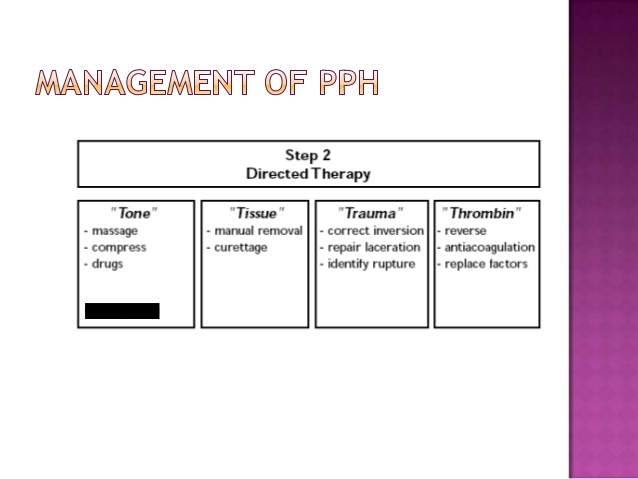
Atony
Trauma - cervical tear, uterine tear, episiotomy, cervical tear
Mixed
Retained placenta
Coagulopathy
Atonic PPH - 80% of PPH
Commonest
Faulty retraction of the uterus
The Four Ts
Tone, Tissue, Trauma, Thrombin
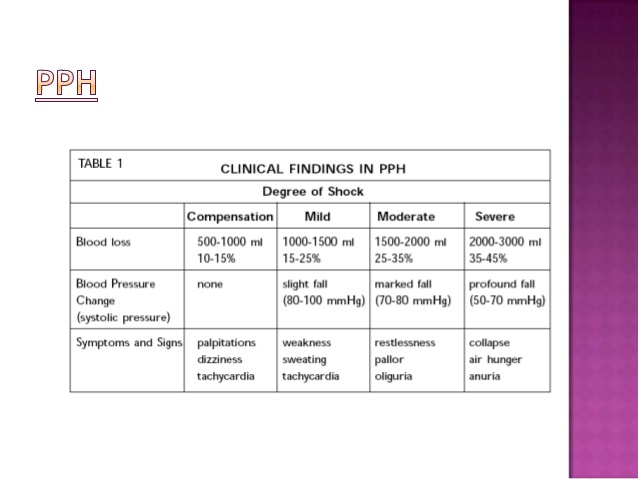
Signs and symptoms
Initially : an increased heart rate,
feeling faint upon standing,
increased breath rate
As more blood is lost the women may feel cold,
blood pressure drops,
Patient may become restless or unconscious.
The condition can occur up to six weeks following delivery.
Management of Postpartum Hemorrhage
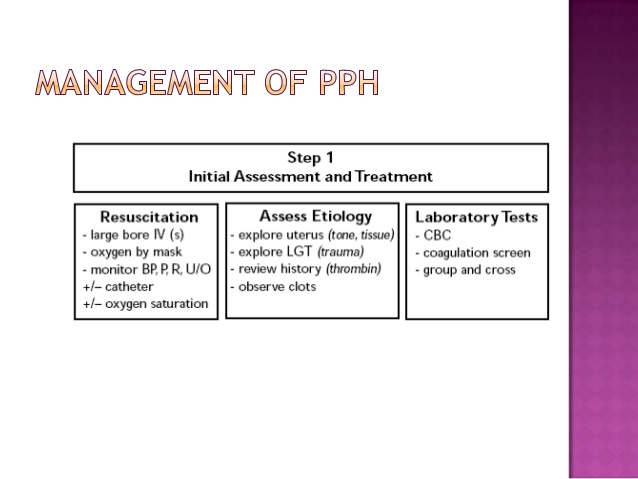
Diagnosis :
assess symptoms,
Find out the cause
Get lab investigations done to find if there is any bleeding disorder, whether there is any DIC, drop in the hematocrit
Medical Interventions
Pitocin
carboprost tromethamine
blood transfusion
Administration of oxygen
Prevention involves decreasing known risk factors
Medication oxytocin to stimulate the uterus to contract shortly after the baby is born.
Misoprostol may be used instead of oxytocin in resource poor settings.
Intravenous fluids,
Blood transfusions, and the medication
Ergotamine
Tranexamic acid decreased a woman's risk of death.
Intravenous oxytocin is the drug of choice for postpartum hemorrhage.
A combination of syntocinon and ergometrine is commonly used as part of active management of the third stage of labour. This is called syntometrine.
Syntocinon alone is a better option.
Giving oxytocin in a solution of saline into the umbilical vein is a method of administering the drugs directly to the placental bed and uterus
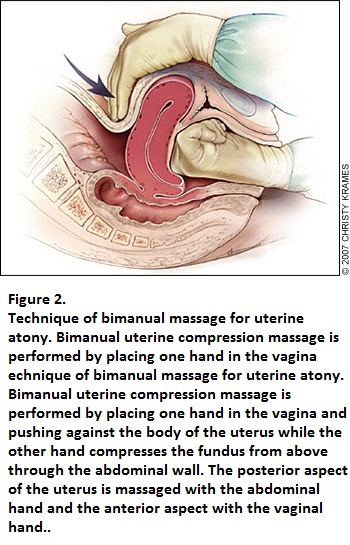
Efforts to compress the uterus using the hands may be effective
The aorta may also be compressed by pressing on the abdomen.
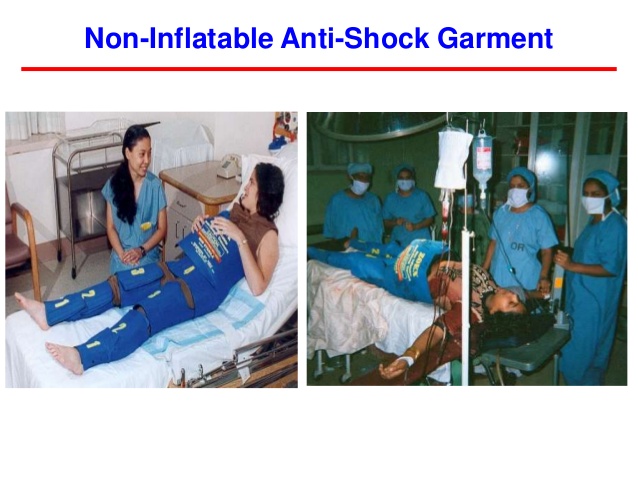
Non-pneumatic anti-shock garment to help until other measures such as surgery can be carried out.
Carbetocin
Tranexamic acid, The benefit was greater when the medication was given within three hours.
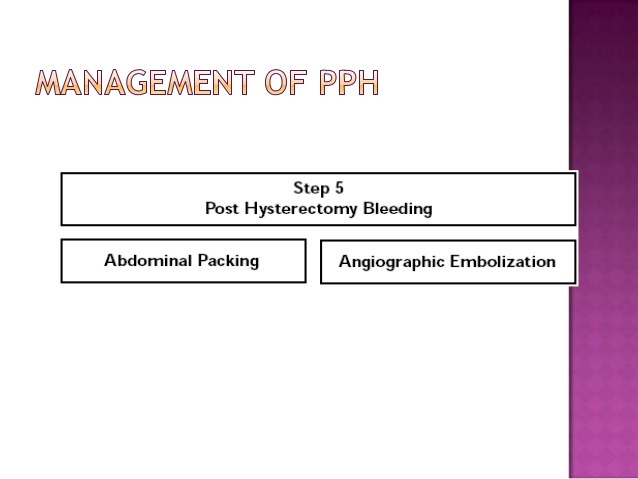
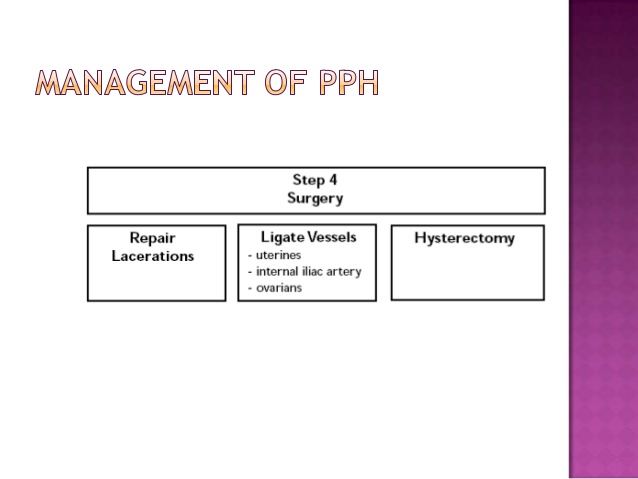
Surgical Management
Hysterectomy
Suturing, Ligation of feeding arteries
Angiographic embolization
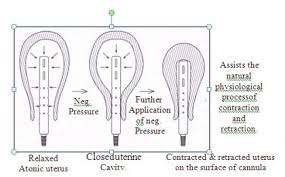
Intrauterine suction cannula with suction (Designed by Dr.Samartharam / Kadampazhipuram / Kerala / India) SR Cannula (Samartha Ram Cannula)
Nursing Management
Nursing Diagnosis : assess the blood loss
Nursing Interventions : save all perineal pads and weigh them to determine the amount of blood loss
Place the mother in lateral position
Assess lochia frequently
Assess vital signs especially pulse and blood pressure
Evaluation : of improvement - BP returing to normal range, normal rate of pulse, flow of lochia less than a saturated pad per hour
Protocol
Stepwise management protocol
of obstetrical hemorrhage after childbirth
Stage 0: normal - treated with fundal massage and oxytocin.
Stage 1: more than normal bleeding - establish large-bore intravenous access, assemble personnel, increase oxytocin, consider use of methergine, perform fundal massage, prepare 2 units of packed red blood cells.
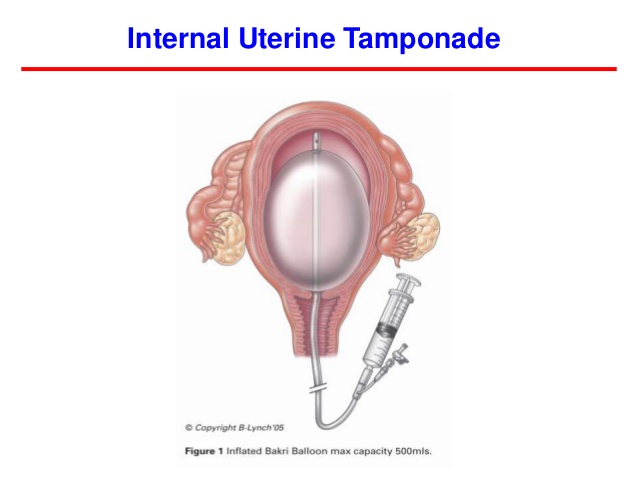
Stage 2: bleeding continues - check coagulation status, assemble response team, move to operating room, place intrauterine balloon, (intrauterine suction cannula and application of suction - in the research level), administer additional uterotonics (misoprostol, carboprost tromethamine), consider: uterine artery embolization, dilatation and curettage, and laparotomy with uterine compression stitches or hysterectomy.
Stage 3: bleeding continues - activate massive transfusion protocol, mobilize additional personnel, recheck laboratory tests, perform laparotomy, consider hysterectomy.
Other measures
Anti-shock measures : non inflatable shock garment, Trendelenberg position, IV fluids, blood transfusion, blood coagulation factors
Bimanual massage of the uterus
.