The Ovary
Definition
Female gonad
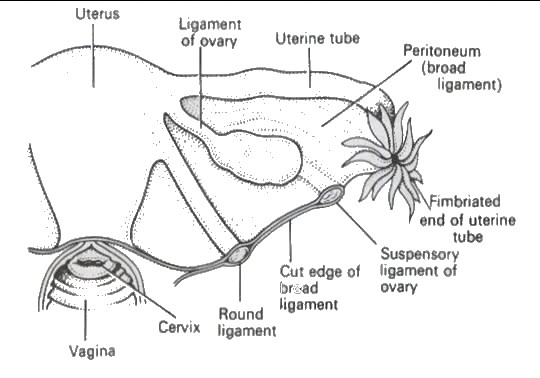
Situation & features
In a shallow fossa on the lateral walls of the pelvis
1 cm x 2 cm x 3 cm (one,two,three)
Attached to the uterus by ovarian ligament
Has mesovarium
Structure and functions
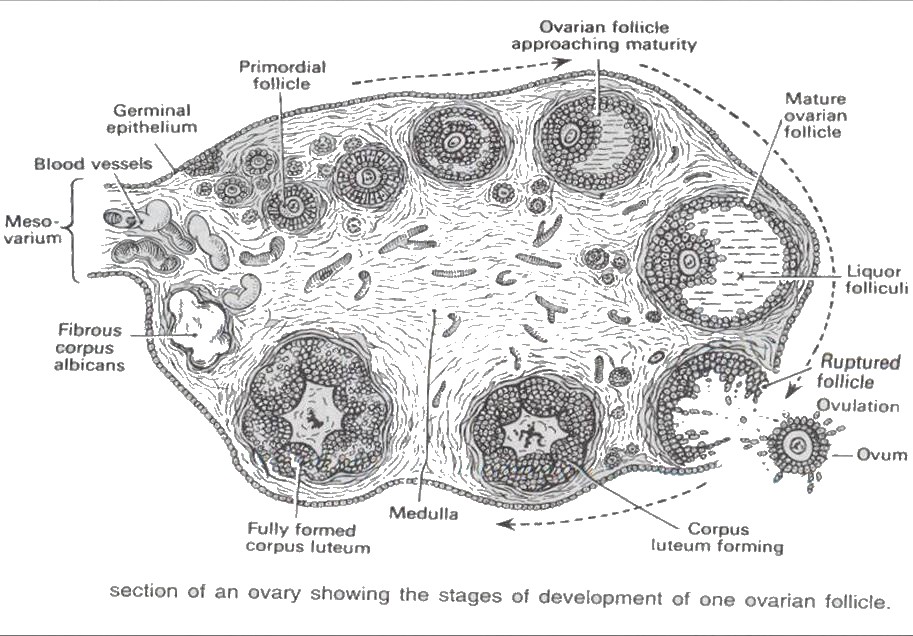
Two layers
medulla - centre - fibrous tissue - blood vessels - nerves
cortex - surrounding the medulla - a frame of connective tissue - contains germinal epithelium - it contains ovarian follicles in various stages of maturity.
Each follicle contains one ovum
Immature follicles are called primordial follicles
During the childbearing years one ovarian follicle (Graafian follicle) matures, ruptures and releases its ovum into the peritoneal cavity. (ovulation)
Blood supply
Ovarian arteries from the abdominal aorta just below the renal arteries
Venous drainage : into a plexus of veins behind the uterus - ovarian veins form - the right ovarian vein opens into the IVC and the left into the left renal vein.
Lymph drainage
Into the lateral aortic and pre-aortic lymph nodes. Lymphatics follow the arteries.
Nerve supply
parasympathetic nerves from sacral outflow
sympathetic nerves from lumbar outflow