Syphilis
Definition
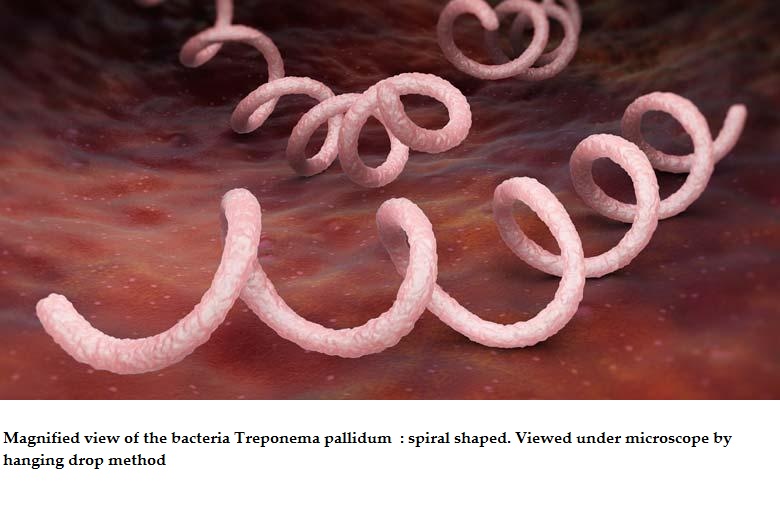
An acute and chronic disease caused by the spirochete Treponema pallidum
Etiology
Acquired through sexual contact
Congenital
Stages of Syphilis
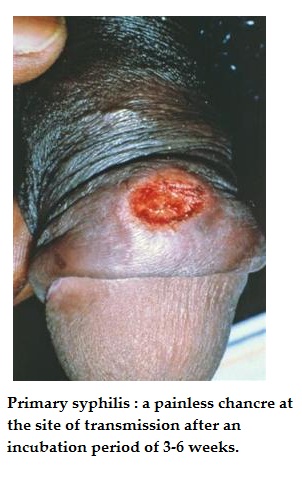
Primary - occurs 2-3 weeks after exposure
A painless ulcer with an underlying button like induration - chancre
Secondary - hematogenous spread of the organism
generalized infection in about 2 to 8 weeks
rashes of secondary siphilis - trunk and extermities, palms, soles
Lymphadenopathy+, arthritis, meningitis, hair loss, fever , malaise weight loss
Followed by a latency period
Tertiary - a slowly progressive inflammatory disease, affects multiple organs
20% to 40% do not exhibit any symptoms or signs
aortitis
neurosyphilis
dementia
psychosis
paresis
stroke
meningitis
Lab Investigation
Serologic tests : Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL)
Rapid Plasma reagin circle Card Test (RPR-CT)
Become negative after adequate therapy nearly about 2 years later
Treponemal tests : Fluorescent Treponemal Antibody Absorption Test (FTA-ABS)
Microhemagglutination Test (MHA-TP)
Medical Management
Penicillin G Benzathine
May need once a week injections x 3
Doxycycline
Nursing Management
Reportable communicable disease
Sexual contacts traced and treated
Lesions of primaryand secondary syphilils - highly infective - wear gloves - hand washing important - no isolation required