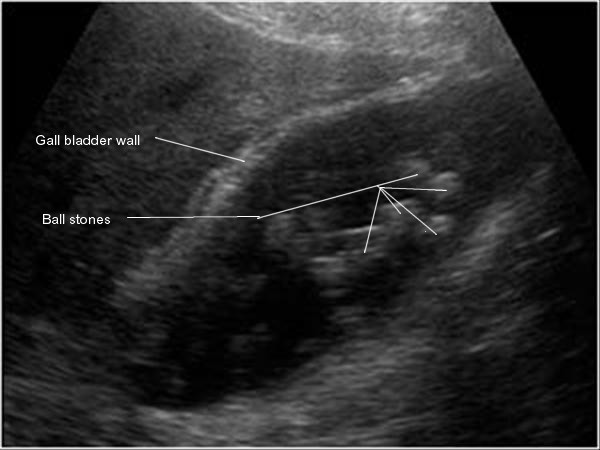
Cholelithiasis
Mr.Rajan 45 years old, diagnosed to have cholelithiasis is posted for cholecystectomy (2 x 15 = 30)
- Define Cholelithiasis
- Mention the risk factors for cholelithiasis
- List down the methods of non surgical removal Gall Stones
- Discuss post operative nursing care of Mr.Rajan
Definition
Formation of stones from the bile is called cholelithiasis
Usually in the gall bladder. May form in the liver or in the biliary passage
Aetiology and Risk Factors
Fat forty fertile
Obesity, more than 40 years of age and multiparity
Oral contraceptives
Oestrogens
Clofibrate
These factors increase biliary cholesterol saturation, decrease bile acid synthesis
Ileal resection or disease
Cystic fibrosis
Diabetes mellitus
Non Surgical Removal of Gall Stones
Infusion of mono-octanoin or methyl tertiary butyl ether into the gallbladder through acatheter inserted percutaneously into the gallbladder
Post-operative residual stone through the T-tube inserted during surgery - using a catheter and an instument with a basket
The sphincter of Oddi is cut through ERCP endoscope the orifice dilated and then a basket
Extracorporeal shock-wave Lithotripsy
Medical Management
Of gallstones has declined in recent years.
A useful alternative to cholecystectomy in select patients, particularly in those who are not suitable surgical candidates or who are unwilling to undergo surgery.
Medical treatments for gallstones, used alone or in combination, include the following :
Oral bile salt therapy (ursodeoxycholic acid) (particularly for x-ray-negative cholesterol gallstones in patients with normal gallbladder function)
Post-operative Nursing Care
After recovery from anaesthesia place the patient in low Fowler's position
Nasogastric suction to relieve abdominal distention
IV fluids
Relieve pain - to combat the ill effects of splinting of the diaphragm by the incisional pain - to prevent pulmonary complications
Look for bleeding Monitor pulse BP - periodically assess the patient for increased tenderness and rigidity of the abdomen
Look for infection : look for loss of appetite, vomiting, pain, distention of the abdoment and temperature elevation
encourage the patient to take deep breaths and cough every hour to expand the lungsfully and prevent atelectasis -us incentive spirometry
Ambulate early to prevent thrombophlebitis
Drainge tube to be made portable and kept always below the lever of the waist level
Water and other fluids given in about 24 hours and a soft diet is started when bowel sounds return
Observe the colour of the stools
I/O Chart
collect urine and stools if needed and send to lab
Low fat diet high carbohydrates and proteins
At discharge : advice to have low fat diet for 6 weeks