Diphtheria
Short Note
Definition
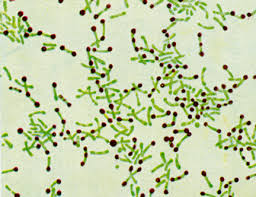
An infection caused by the bacterium Corynebacterium diphtheria.
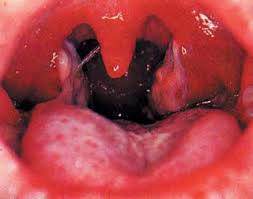
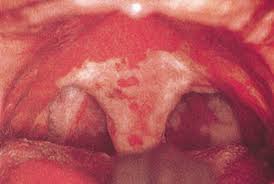
Causing sore throat and fever. In severe cases forms a grey or white patch in the throat.
Pathophysiology
Spreads by direct contact or through the air, by contaminated objects
Some people carry the bacteria without having symptoms, but can still spread the disease to others.
Start two to five days after exposure.
This can block the airway and create a barking cough as in croup.
The neck may swell in part due to large lymph nodes.
A form of diphtheria that involves the skin, eyes, or genitals also exists.
Diphtheria can also cause paralysis in the eye, neck, throat, or respiratory muscles
The symptoms are due to a toxin produced by the bacteria. diphtheria toxin spreads through the blood
There are three main types of C. diphtheriae causing different severities of disease.
Complications
Myocarditis - an abnormal heart rate
Inflammation of nerve - paralysis
Kidney problems
Bleeding problems due to low blood platelets.
Severe symptoms and complications are the result of toxins produced by the bacteria
Signs and Symptoms
Fever of 38 °C or above,
chills,
fatigue,
bluish skin coloration (cyanosis),
sore throat, hoarseness,
cough, a brassy or "barking" cough, stridor
headache,
difficulty swallowing, painful swallowing, swollen neck and throat, or "bull neck"
difficulty breathing, rapid breathing,
foul-smelling bloodstained nasal discharge
lymphadenopathy,
cardiac arrhythmias, myocarditis. Abnormal cardiac rhythms can occur early in the course of the illness or weeks later, and can lead to heart failure
cranial and peripheral nerve palsies.
Diphtheritic croup
A diphtheria skin lesion on the leg
Diagnosis
The appearance of the pseufomembrane in the throat with confirmation by culture : Isolation of Corynebacterium diphtheriae from a throat swab.
Treatment
Prevention : A vaccine, diphtheria toxoid, is effective for prevention : administered along with vaccines for tetanus and pertussis (DPT : Triple Antigen) on months 4,5,6 of the baby
Treatment : erythromycin or penicillin G.
Procaine penicillin G given intramuscularly for 14 days (300,000 U/d for patients weighing <10 kg and 600,000 U/d for those weighing >10 kg). Patients with allergies to penicillin G or
can use erythromycin rifampin or clindamycin.
tracheostomy is sometimes needed to open the airway in severe cases.
obstruction in the throat may require intubation or a tracheotomy
Prognosis
Diphtheria is fatal in between 5% and 10% of cases. In children under five years and adults over 40 years, the fatality rate may be as much as 20%.