Abruptio Placentae
Definition
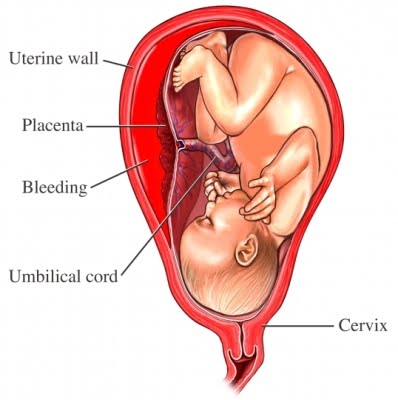
Separation of the placenta from the site of implantation before delivery
Also called premature separation of placenta/accidental hge/ablatio placentae/placental abruption
Incidence
9 in 1000 pregnancies
usually in 3rd trimester; anytime after 20th week
After 1 abruptio placentae the chance of having it is 4-17% in the next pregnancy and 25% in the third pregnancy
Risk Factors
Multiparity
Hypertension
Blunt external abdominal trauma
Smoking
Poor nutrition
> 35 yrs of age
Short umbilical cord
Cocaine
Previous third trimester bleeding
Alcohol use
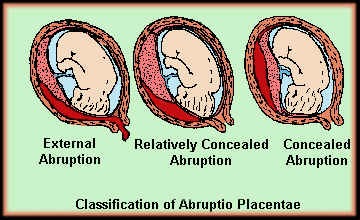
Types
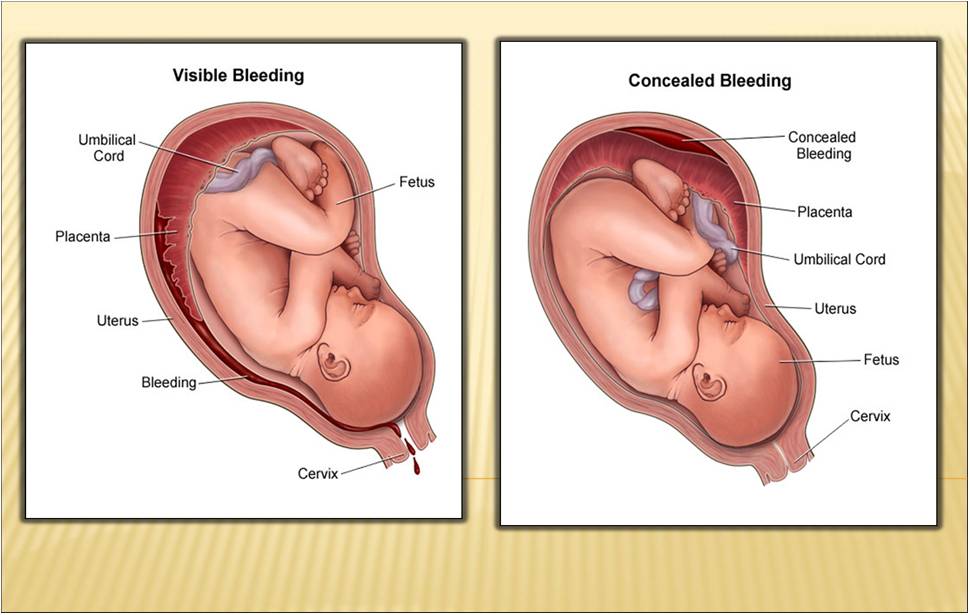
Central : placenta separates centrally - blood trapped between placenta and uterine wall - concealed bleeding - concealed type
Complete : total separation - massive vaginal bleeding - revealed type
Signs and Symptoms
Sharp abdominal pain/back pain (leakage of blood into peritoneal cavity, through uterine wall), tender abdomen, abdomen tense (board like)
Tenderness of the uterus
Vaginal bleeding painful
Rapid uterine contractions, often coming one right after another
Fetal distress - due to reduction of blood supply to fetus - altered FHR
Couvelaire uterus (blood infiltrating the uterine musculature) - leadin to uterus becoming hard like a board without apparent bleeding
Complications
Maternal :
In revealed type : hypovolemia, shock
In concealed type : haemorrhage, shock, blood coagulation disorders, oliguria and anuria, postpartum hge, puerperal sepsis
Shock may lead to kidney failure
Fetal :
Fetal hypoxia
Premature birth
Stillbirth
Management
Keep the woman in lateral position
O2 to limit fetal hypoxia
Monitor FHT, VS
Have a basline fibrinogen check
No IE or rectal examination, no enema
Keep vein patent with IV Fluids
Medical Management
Hospitalize
Monitor for increasing placental separation
USGM : to differentiate between abruptio placentae and placenta previa
Monitor FHR
Monitor vital signs
Check urine output, hematocrit, platelet count and fibrinogen concentration
Blood transfusion if needed
Surgical Management
Classical Cesarian Section - if transverse lie, multiple fetuses, low anterior placenta, varicosities of the lower segment or cervical tumors
Lower segment Cesarian in the absence of the above contraindications
Prevention
Avoid drinking, smoking
Regular prenatal check-ups
Control of BP
Prenatal vitamins with folate
* * * * * * * * * * * *