Shock
Definition
A condition in which the systemic blood pressure is inadequate to deliver oxygen and nutrients to support vital organs and cellular function.
Due to
Inadequate blood flow to the tissues
Inadequate cardiac pumping
Ineffective vasculature/circulatory system
Insufficient blood volume
Classification
Hypovolemic shock - decreased blood volume
Cardiogenic shock - inadequate pumping of blood by the heart
Circulatory shock - maldistribution or mismatch of blood flow to the cells
Obstructive shock - dissecting aneurysm, cardiac tamponade, tension pneumothorax
Anaphylactic shock - allergic reaction
Pathophysiology
Shock - inadequate blood supply - cells deprived of O2 and nutrients - anaerobic metabolism - low energy yields from nutrients - acidotic intracellular environment - normal cell function stops - mitochondria damaged - cell death
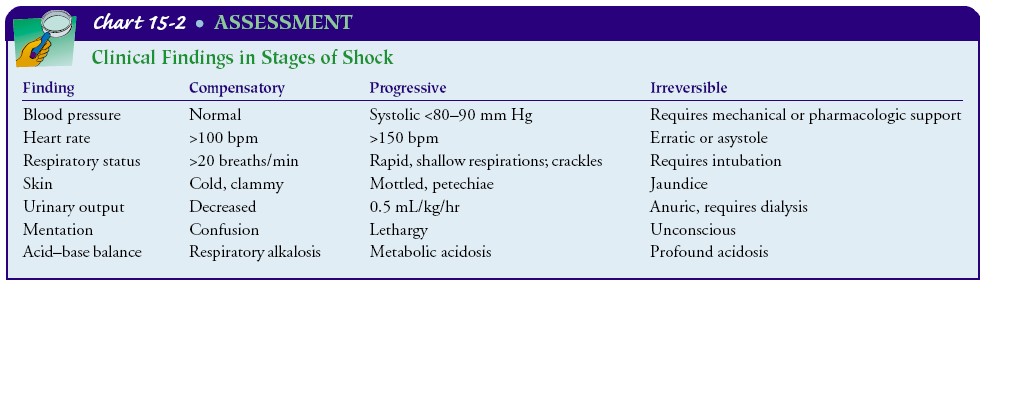
Stages of Shock
Compensatory stage - BP normal - Vasoconstriction (cold clammy hands, bowel sounds hypoactive, decreased urine output) increased heart rate, "fight or flight" response - blood from skin, kidney and GIT shunted to brain and heart - metabolic acidosis - Respiratory rate increases - compensatory respiratory alkalosis - confusion - treatment begun now good prognosis - identify the cause of shock and treat - fluid replacement and medications
Progressive stage - mechanisms that regulate BP can no longer compensate -- Systolic BP falls below 90 mm Hg - failure of the cardiac pump - increased capillary permeability - interstitial edema - cardiac input reduces - respiration rapid and shallow - pulmonary creps + - surfactant reduces - alveoli collapse - called acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) - dysrrhythmias - ischaemia - chest pain - CPK-MB and Tn-I rise - mental status deteriorates due to hypoxia - pupils dilate - sluggish reaction - kidney starts failing - urinary output below 0.5 ml/kg/per hour (below 30 ml/hour) - liver starts failing, fails to filter bacteria - infection - Jaundice may be seen - GIT ischaemia - stress ulcers in stomach - small intestinal mucosa becomes necrotic - bloody diarrhoea - bacterial toxins from intestine spreads to other parts
Irreversible stage - (refractory) - organ damage is very severe - No response to treatment - BP remains low - complete renal and liver failure - necrotic tissue toxins released - metabolic acidosis - lactic acidosis supevenes - all organs fail and death is imminent
Nursing Management
ICU
Hemodynamic monitoring
ECG monitoring
ABG
Serum electrolytes
Physical and mental changes noted
Supportive technologies used - mechanical ventilation, dialysis, intra-aortic balloon pump
Vital signs monitored every 15 mts
Promote rest and comfort - minimize physical activity - temperature extremes avoided,
ensure safe administration of fluids, medications
Document the fluids and drugs given
Maintain Modified Trendelenburg position
Check the fluids and blood (groupe and Rh type) and warmth
Cardiovascular overload and pulmonary oedema avoided
Nutritional support to meet higher demands of energy during shock : >3000 cals/day
O2
Prevent allergic reactions to drugs by detailed history taking
Support family members
Medical Management
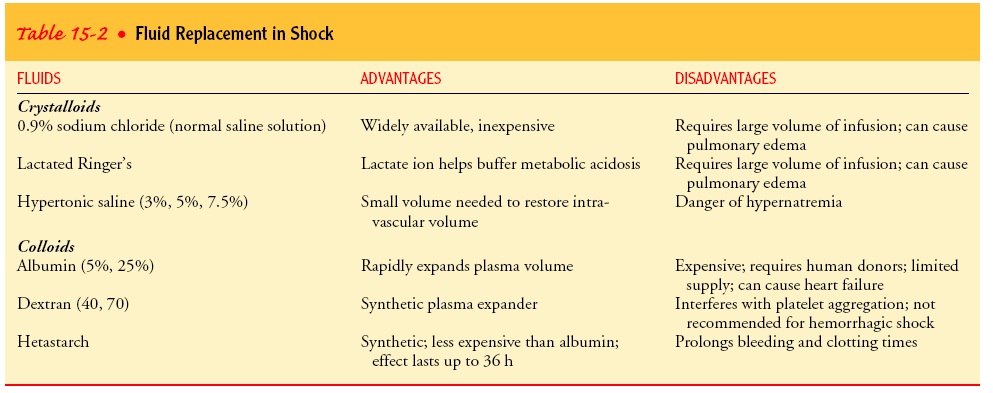
Normal Saline
Ringer Lactate
Colloids - Volume expanders -
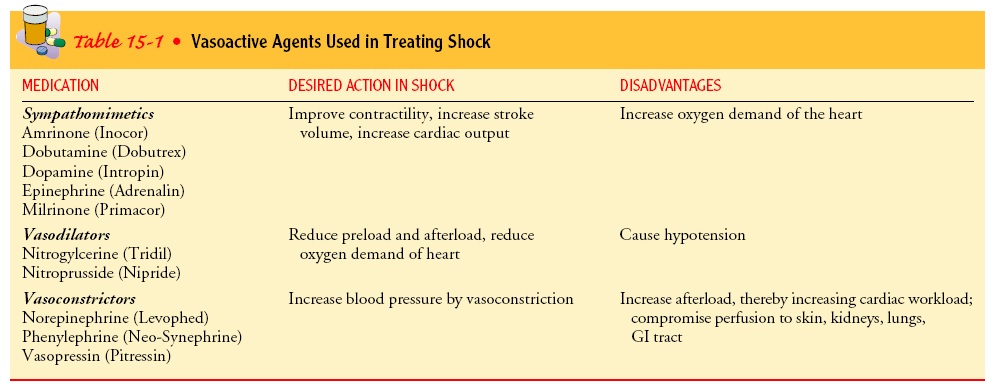
Vasoactive Medication Therapy
Indicated when fluid therapy alone cannot maintain adequate MAP
To improve contractility, increase stroke volume, increase cardiac output
Sympathomimietics :
Amrinone (inocor)
Dobutamine (Dobutres)
Dopamine (Intropin)
Epinephrin (Adrenaline)
Milrinone (Primacor)
To Reduce preload and afterload, reduce oxygen demand of heart
Vasodilators :
Nitroglycerine (Tridil)
Nitroprusside (Nipride)
To increase blood pressure by vasoconstriction
Vasoconstrictors :
Norepinephrine
Phenylephrine
Vasopressin (Pitressin)
Hypovolemia due to bleeding : Control bleeding;
Dehydration : Treat Underlying cause of dehydration like diarrhoea, vomiting, diabetic ketoacidosis etc : Blood, colloids, crystalloids
Cardiogenic Shock
Tamponade relieved
Infarction : further myocardial damage is prevented; contractility of the myocardium is increased and afterload is decreased; thrombolytic therapy instituted; angioplasty/ bypass surgery; dysrrhythmia corrected
Control Chest pain if present
Alleviate anxiety
Contol heart rate - medication or pacemaker
Implement mechanical cardiac support ( intra-aortic balloon counterpulsation therapy, ventricular assist systems, or extrcorporeal cardiopulmonary bypass)
Anaphylactic Shock
Avoid substances that has caused antigen antibody reaction earlier
Epinephrin is used to cause vasoconstriction during the shock
Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) - to reverse effects of histamine - given IV
For bronchospasm Nebulization with albuterol (Proventil)
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation if needed
Endotracheal intubation with or without tracheostomy may be needed
304